ফিরে আসা (লাশ হয়ে দেশে) Probashir Lash
গল্প: ফিরে আসা (লাশ হয়ে দেশে) প্রথম অংশ: স্বপ্নের ডানায় ভর করে বাবা দরজার সামনে দাঁড়িয়ে। হাতে একটি ছোট্ট ব্যাগ, আর…
এইট সিম সিঙ্গাপুর রিভিউ: স্থানীয়, প্রবাসী ও পর্যটকদের জন্য সেরা ভ্যালু সিম ও ই-সিম প্ল্যান Eight Sim
এইট সিম সিঙ্গাপুর রিভিউ: স্থানীয় ও পর্যটকদের জন্য সেরা ভ্যালু সিম ও ই-সিম প্ল্যান কেন এইট সিম সিঙ্গাপুরের মোবাইল …
সিঙ্গাপুর পুংগল কন্ডোমিনিয়ামে আগুন, শতাধিক বাসিন্দা সরানো হয়েছে; ৩ জন হাসপাতালে ভর্তি
বুধবার, ৬ আগস্ট ২০২৫ সন্ধ্যায়, সিঙ্গাপুরের পুংগল ফিল্ড ওয়াকের একটি ১৬ তলা ইউনিটে ভয়াবহ অগ্নিকাণ্ড ঘটে। ইউনিটটি ওয়াটার…
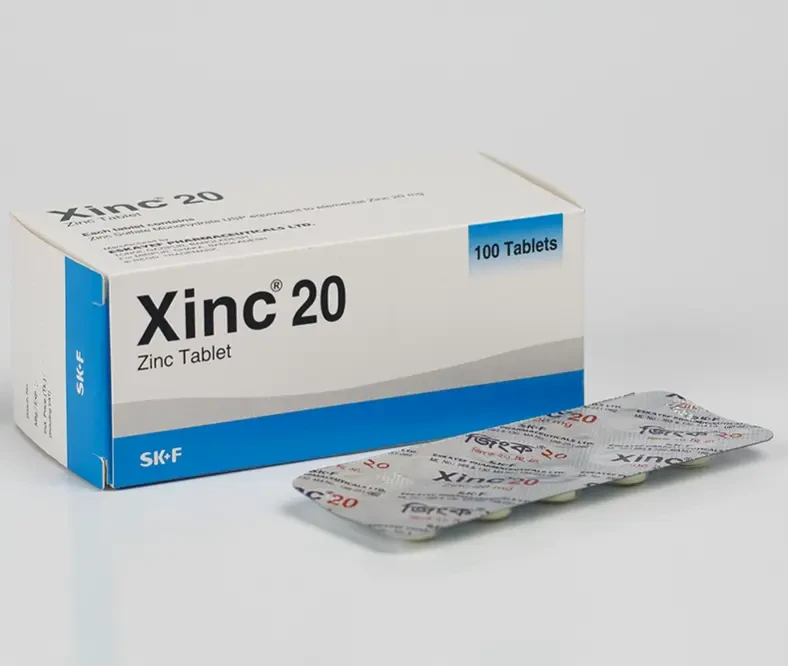
সর্দি ও জ্বর হলে কী ওষুধ খাওয়া উচিত
সর্দি ও জ্বরের জন্য সবচেয়ে কার্যকর ওষুধ – বাংলাদেশে জনপ্রিয় চিকিৎসা পদ্ধতি 🔍 সর্দি ও জ্বর – আমাদের দৈনন্দিন জীবনে প…
সিঙ্গাপুরে ট্রেইনিং রেকর্ড এবং সার্টিফিকেট চেক করার সম্পূর্ণ গাইড (২০২৫ আপডেটেড)
🎓 সিঙ্গাপুরে ট্রেইনিং রেকর্ড এবং সার্টিফিকেট চেক করার সম্পূর্ণ গাইড (২০২৫ আপডেটেড) সিঙ্গাপুরে যারা Workplace Safet…
Toa Payoh HDB ফ্ল্যাটে ভয়াবহ অগ্নিকাণ্ড, সাতজন হাসপাতালে ভর্তি
সিঙ্গাপুর, ২৯ জুলাই ২০২৫ (মঙ্গলবার): আজ দুপুরে সিঙ্গাপুরের টোৱা পায়ো এলাকায় একটি HDB ফ্ল্যাটে ভয়াবহ অগ্নিকাণ্ডের ঘট…
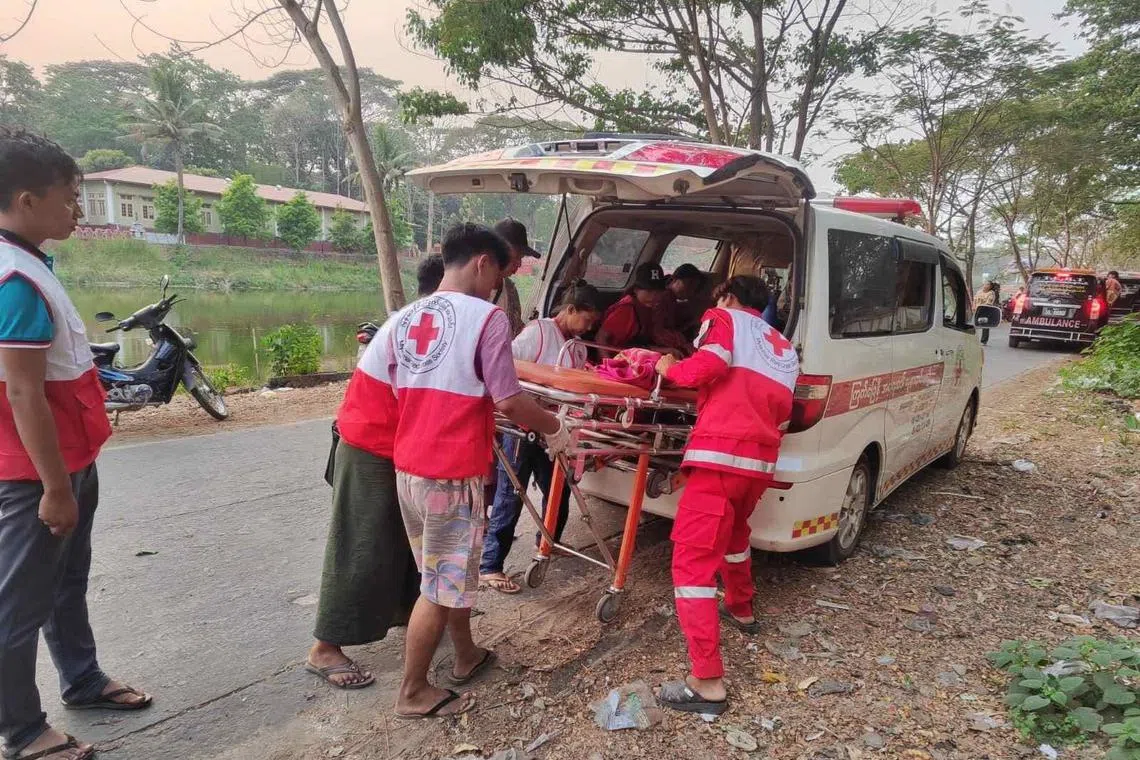
সিঙ্কহোল দুর্ঘটনায় নারীকে বাঁচালেন এক ভারতীয় কর্মী – সাহসী উদ্ধার অভিযান সবার প্রশংসা কুড়ালো
সিঙ্কহোল দুর্ঘটনায় নারীকে বাঁচালেন এক ভারতীয় কর্মী – সাহসী উদ্ধার অভিযান সবার প্রশংসা কুড়ালো সিঙ্গাপুর, ২৬ জুলাই – …
বিমানবন্দরে যাত্রী বিদায়-স্বাগত: ডিপারচার ও এরাইভাল পয়েন্টে নতুন নির্দেশনা
বিমানবন্দরে যাত্রী বিদায়-স্বাগত: ডিপারচার ও এরাইভাল পয়েন্টে নতুন নির্দেশনা ২৭ জুলাই থেকে কার্যকর ঢাকা, ২৫ জুলাই ২০…
প্রবাসী শ্রমিকদের জন্য জরুরি তথ্য: SATA PCP-র আওতায় চিকিৎসা সেবা গ্রহণে অ্যাপয়েন্টমেন্ট প্রয়োজন
📢 প্রবাসী শ্রমিকদের জন্য জরুরি তথ্য: SATA PCP-র আওতায় চিকিৎসা সেবা গ্রহণে অ্যাপয়েন্টমেন্ট প্রয়োজন সিঙ্গাপুরে কর্ম…
SCDF Rescues Two Workers After Gondola Cable Snaps at Raffles City Tower
Headline: SCDF Rescues Two Workers After Gondola Cable Snaps at Raffles City Tower By: Thedaily71| Date: 21 July 2025…
মুখ দিয়ে লালা পড়া বন্ধ করার উপায়: সম্পূর্ণ ঘরোয়া ও চিকিৎসা গাইড
মুখ দিয়ে লালা পড়া বন্ধ করার উপায়: সম্পূর্ণ ঘরোয়া ও চিকিৎসা গাইড মুখ দিয়ে লালা পড়া (ড্রোলিং বা সায়ালোরিয়া) একটি…
Why Many Companies Fail to Value Honest and Competent Employees | কেন সৎ ও দক্ষ কর্মীরা মূল্য পায় না
🏢 Why Many Companies Fail to Value Honest and Competent Employees 👉 Keywords: why honest employees are ignored co…
প্রেজেন্টেশন ভয় কাটানোর ৭টি কার্যকর উপায়
প্রেজেন্টেশন দিতে ভয় পান? এর থেকে মুক্তির কার্যকর ৭টি উপায় আজকের যুগে প্রেজেন্টেশন বা উপস্থাপনা শুধুমাত্র শিক্ষক বা …
কিসমিস ভেজানো পানি পান করার ১০টি চমৎকার উপকারিতা
📰 কিসমিস ভেজানো পানি পান করার ১০টি চমৎকার উপকারিতা – প্রতিদিন সকালে খালি পেটে খান, থাকুন সুস্থ ও সতেজ! 📅 তারিখ: ১…
Listen Live Radio
আরো চ্যানেল যুক্ত করতে বা আপনার মতামত জানাতে
ক্লিক করুন এখানেNo Station Playing
| Radio Icon | Station Name | Action |
|---|---|---|
| ঐশী বাণী | ||
 |
রেডিও সুফিবাদ | |
| দৈনিক আন নূর | ||
 |
Jamat Raza-E-Mustafa | |
 |
বাংলাদেশ বেতার (ক) | |
 |
Peoples Radio | |
 |
BBC Radio Asian Network | |
 |
Akashvani Maitree | |
 |
বাংলাদেশ বেতার (খ) | |
 |
বাংলাদেশ বেতার ট্রাফিক সম্প্রচার | |
 |
Radio Bhumi | |
 |
Dhaka FM | |
 |
Radio Mahananda | |
 |
Radio Foorti | |
 |
Bisme Islamic Radio | |
 |
CNA 938 | |
 |
BBC World | |
 |
ময়মনসিংহ এফএম ৯২.০ | |
 |
ঈদের গান |
Featured post
Popular Posts

সর্দি ও জ্বর হলে কী ওষুধ খাওয়া উচিত
ফিরে আসা (লাশ হয়ে দেশে) Probashir Lash
Categories
- News (283)
- Lifestyle (157)
- Diseases And Treatment (76)
- Computer Tips (45)
- ঈমান ও ইসলাম (43)
- Story (30)
- Business Tips (26)
- Safety (26)
- Poem (24)
- Website Development (22)
- Singapore (20)
- Biography (14)
- Jokes (14)
- Bangladesh (11)
- Job (11)
- আধুনিক গান (9)
- Mobile (6)
- Online Earnings (5)
- International (2)
- প্রবাসী খবর (1)
সিঙ্গাপুরে ট্রেইনিং রেকর্ড এবং সার্টিফিকেট চেক করার বিস্তারিত গাইড

Bangla date add in your website HTML tips.
Safe work procedure for ferrying workers by lorry in singapore
বাংলাদেশি শ্রমিকদের জন্য সিঙ্গাপুরে কম খরচে দাঁতের চিকিৎসা
Safety
Explore More Post

Rahman Mahabubur (Mahabub)
📧 Personal: mahabub.safety@hotmail.com
🏢 Official: info.thedaily71@gmail.com
📱 Mobile: +6584000037 🌏Web: Thedaily71
© 2025 TheDaily71. All Rights Reserved.
Original content is the property of TheDaily71 and may not be reproduced without permission. Third-party content remains the property of its respective owners and is used with proper attribution. For concerns, please contact us.
































Social Plugin